Pneumatic systems are systems that operate using the power of compressed air. These systems are used in many different areas to provide mechanical motion and power. The working principle of pneumatic systems is quite simple.
Basic Components of Pneumatic Systems:
- Compressor: Compresses and pressurizes the air.
- Air Tank: Stores compressed air.
- Valves: Controls the flow of air.
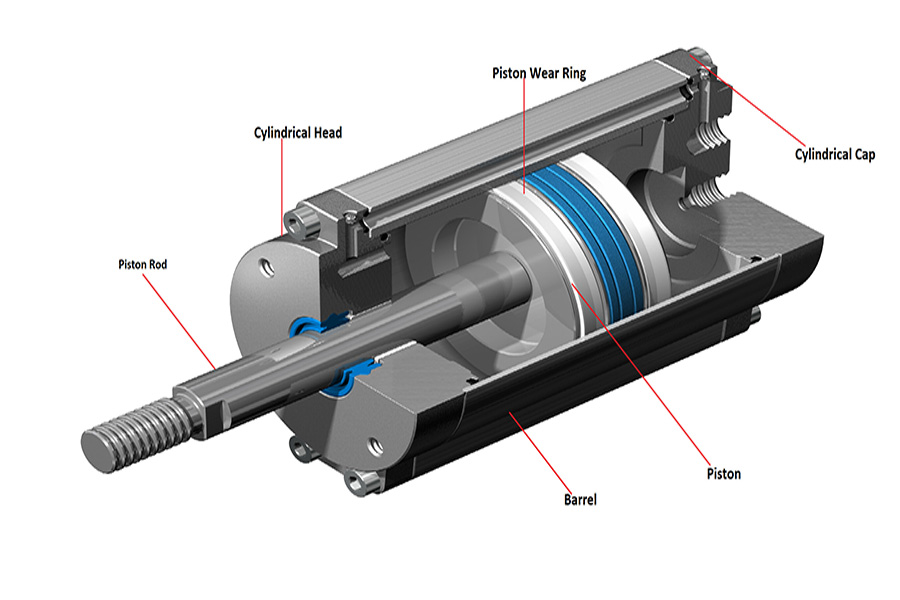
- Actuators: Converts the air pressure into mechanical motion.
- Pipes and Hoses: Allows the air to be transported.
Working Stages of Pneumatic Systems:
- Air Compression: The compressor takes in atmospheric air and compresses it to pressurize it.
- Air Storage: Compressed air is stored in the air tank.
- Air Control: Valves control the flow of compressed air in the air tank and direct it to where it is needed.
- Air Usage: The air pressure is converted into mechanical motion by actuators.
- Air Exhaust: Used air is vented to the atmosphere.
Advantages of Pneumatic Systems:
- Safe: Pneumatic systems are safer than electrical systems. There is no risk of explosion with air, and there is also no risk of electric shock with pneumatic systems.
- Clean: Pneumatic systems are cleaner than hydraulic systems. There is no oil or other contaminants in the air.
- Efficient: Pneumatic systems use energy efficiently. Compressed air can be stored and reused after work is done.
- Flexible: Pneumatic systems can be adapted to a wide variety of applications. Pneumatic actuators are available in different sizes and powers.
- Affordable: Pneumatic systems are more affordable than other automation systems.
Disadvantages of Pneumatic Systems:
- Risk of Leakage: There is always a risk of leakage in pneumatic systems. Leaks reduce the efficiency of the system and lead to energy loss.
- Noise: Pneumatic systems can generate noise during operation.
- Speed: Pneumatic systems can be slower than hydraulic systems.
Application Areas of Pneumatic Systems:
Pneumatic systems are used in many different areas. The main areas of use are:
- Industry: Pneumatic systems are widely used in production lines, robotics, assembly lines, automation systems, air tools, and conveyor systems.
- Construction: Pneumatic systems are used in drills, hammers, sanders, and other construction tools.
- Medical: Pneumatic systems are used in dental instruments, ventilators, and other medical devices.
- Transportation: Pneumatic systems are used in truck brakes, airbags, and automatic doors.
- Agriculture: Pneumatic systems are used in spraying, fertilizing, irrigation, and harvesting.
Conclusion:
Pneumatic systems are a versatile technology that can be used in many different areas. They have many advantages such as being safe, clean, efficient, flexible, and affordable. Therefore, pneumatic systems are an ideal choice for many different applications.
